Hormones
within
the
human
body
dictate
many
actions.
Certain
hormones
are
responsible
for
appetite,
hunger,
and
satiety.
Every
person
must
understand
these
hormones
and
their
role
in
weight
management.
Ghrelin
and
leptin
are
the
two
primary
hormones.
What
should
a
person
know
about
them
to
get
their
weight
under
control
and
keep
it
there?
Ghrelin
plays
a
critical
role
in
appetite
regulation
and
metabolism.
Known
as
the
hunger
hormone,
ghrelin
is
produced
primarily
in
the
stomach
and
signals
the
brain
when
it
is
time
to
eat.
Levels
of
this
hormone
fluctuate
throughout
the
day,
rising
before
meals
and
decreasing
after
eating.
Anyone
looking
to
manage
weight
effectively
must
understand
how
ghrelin
functions
and
what
factors
influence
its
production.
Ghrelin

level
of
ghrelin
depends
on
many
factors
Ghrelin
communicates
directly
with
the
hypothalamus,
the
part
of
the
brain
that
controls
hunger,
metabolism,
and
energy
balance.
When
the
stomach
is
empty,
ghrelin
levels
surge,
prompting
a
strong
urge
to
eat.
After
consuming
food,
ghrelin
levels
drop,
reducing
the
feeling
of
hunger.
However,
the
speed
and
efficiency
of
this
process
depend
on
several
factors,
including
diet,
sleep,
and
stress
levels.
Beyond
stimulating
appetite,
ghrelin
also
affects
digestion,
insulin
sensitivity,
and
even
mood.
Some
research
suggests
that
high
ghrelin
levels
contribute
to
food
cravings,
particularly
for
calorie-dense,
high-fat
foods.
Understanding
these
mechanisms
provides
insight
into
why
some
people
struggle
with
constant
hunger
even
after
eating.
Factors
That
Increase
Ghrelin
Levels
Ghrelin
production
is
influenced
by
multiple
lifestyle
factors,
many
of
which
people
can
control
to
regulate
appetite
more
effectively.
-
Poor
Sleep:
Lack
of
sleep
triggers
a
rise
in
ghrelin,
making
people
feel
hungrier
throughout
the
day.
Sleep
deprivation
also
decreases
leptin,
the
hormone
responsible
for
signaling
fullness,
creating
a
perfect
storm
for
overeating. -
High
Stress:
Chronic
stress
elevates
ghrelin
levels,
leading
to
stress-induced
eating.
Many
people
under
stress
experience
cravings
for
high-calorie
foods
due
to
the
hormone’s
effect
on
dopamine
release,
which
creates
a
temporary
feeling
of
pleasure. -
Dieting
and
Caloric
Restriction:
Extreme
calorie-cutting
can
cause
ghrelin
levels
to
spike,
making
sustained
weight
loss
difficult.
The
body
reacts
to
prolonged
caloric
deficits
by
increasing
hunger
signals,
encouraging
overeating
once
normal
eating
patterns
resume. -
Meal
Timing:
Long
gaps
between
meals
allow
ghrelin
to
rise,
intensifying
hunger
signals
and
increasing
the
likelihood
of
overeating
at
the
next
meal.
Regulating
Ghrelin
for
Better
Weight
Control
Managing
ghrelin
levels
is
key
to
preventing
constant
hunger
and
achieving
long-term
weight
stability.
Practical
strategies
can
help
regulate
this
hormone
and
support
a
healthier
relationship
with
food.
-
Prioritize
Protein:
High-protein
meals
reduce
ghrelin
levels
more
effectively
than
meals
rich
in
carbohydrates
or
fats.
Protein
provides
lasting
satiety
and
helps
curb
cravings
throughout
the
day. -
Stay
Hydrated:
Dehydration
often
mimics
hunger,
causing
unnecessary
food
intake.
Drinking
enough
water
throughout
the
day
helps
control
appetite
and
supports
metabolism. -
Eat
Consistently:
Regular,
well-balanced
meals
prevent
extreme
fluctuations
in
ghrelin,
keeping
hunger
levels
more
stable. -
Exercise
Regularly:
Physical
activity
plays
a
role
in
ghrelin
regulation
by
reducing
stress,
improving
sleep,
and
promoting
overall
hormonal
balance.
Personalized,
medically-supervised
weight
loss
therapy
can
help
individuals
manage
ghrelin
more
effectively
by
addressing
unique
hormonal
imbalances
and
metabolic
needs.
Services
like
yuniquemedical.com
offer
tailored
approaches
that
consider
individual
factors,
including
ghrelin
sensitivity,
to
optimize
weight
management
strategies.
Leptin
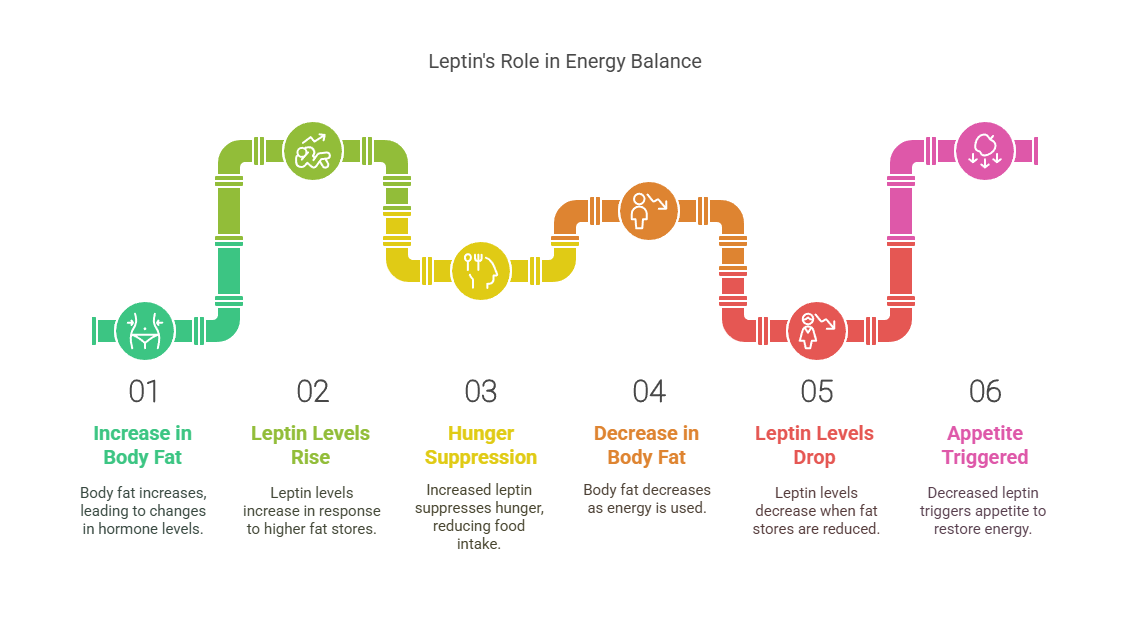
leptin
prevents
overeating
Leptin
signals
the
brain
when
the
body
has
enough
energy.
Fat
cells
produce
this
hormone,
releasing
it
into
the
bloodstream
to
communicate
with
the
hypothalamus.
When
leptin
functions
properly,
it
prevents
overeating
by
reducing
hunger
after
meals.
How
Leptin
Works
Leptin
acts
as
a
regulator
of
long-term
energy
balance.
As
body
fat
increases,
leptin
levels
rise,
suppressing
hunger.
When
fat
stores
decrease,
leptin
drops,
triggering
appetite
to
restore
energy
reserves.
Unlike
ghrelin,
which
responds
to
short-term
meal
timing,
leptin
provides
a
broader
signal
about
the
body’s
overall
energy
status.
Leptin
Resistance
Many
people
struggle
with
leptin
resistance,
where
the
brain
stops
responding
to
high
leptin
levels.
Even
with
plenty
of
stored
energy,
hunger
persists.
This
condition
is
common
in
obesity
and
makes
weight
loss
difficult.
Several
factors
contribute
to
leptin
resistance:
-
Chronic
Inflammation:
Excess
body
fat
leads
to
inflammation,
disrupting
leptin
signaling. -
Processed
Foods:
Diets
high
in
refined
carbohydrates
and
unhealthy
fats
interfere
with
leptin
sensitivity. -
Lack
of
Sleep:
Poor
sleep
reduces
leptin
levels
while
increasing
ghrelin,
driving
overeating. -
No
Physical
Activity:
A
sedentary
lifestyle
impairs
leptin
function,
making
appetite
harder
to
control.
Resetting
Leptin
Sensitivity
Restoring
leptin
balance
helps
control
appetite
and
prevent
overeating.
Key
strategies
include:
-
Prioritizing
Whole
Foods:
A
diet
rich
in
protein,
fiber,
and
healthy
fats
supports
leptin
function. -
Getting
Enough
Sleep:
At
least
seven
hours
per
night
keeps
leptin
and
ghrelin
in
balance. -
Exercising
Regularly:
Physical
activity
improves
leptin
sensitivity,
reducing
hunger
signals. -
Reducing
Inflammation:
Cutting
processed
foods
and
managing
stress
helps
restore
leptin
function.
The
Relationship
Between
Ghrelin
and
Leptin
Ghrelin
and
leptin
work
together
to
regulate
appetite
and
energy
balance.
Ghrelin
stimulates
hunger,
signaling
the
need
for
food,
while
leptin
suppresses
appetite,
letting
the
brain
know
when
enough
energy
has
been
consumed.
A
proper
balance
between
these
hormones
is
essential
for
maintaining
a
stable
weight.
How
Imbalances
Lead
to
Overeating
When
ghrelin
levels
remain
high
and
leptin
signaling
is
weak,
hunger
persists
even
after
meals.
Several
factors
contribute
to
this
imbalance:
-
Sleep
Deprivation:
Inadequate
sleep
raises
ghrelin
while
lowering
leptin,
increasing
hunger
and
cravings. -
Poor
Diet
Choices:
Processed
foods
and
excess
sugar
disrupt
leptin
sensitivity,
making
the
body
resistant
to
fullness
signals. -
Chronic
Stress:
Elevated
cortisol
levels
interfere
with
both
hormones,
leading
to
emotional
eating. -
Extreme
Dieting:
Severe
calorie
restriction
causes
ghrelin
to
spike
while
suppressing
leptin,
making
long-term
weight
loss
harder.
Restoring
Hormonal
Balance
Controlling
appetite
requires
maintaining
the
right
ratio
of
ghrelin
to
leptin.
Several
strategies
support
this
balance:
-
Eating
Whole
Foods:
Protein,
fiber,
and
healthy
fats
keep
hunger
under
control
and
improve
leptin
sensitivity. -
Maintaining
a
Consistent
Meal
Schedule:
Skipping
meals
allows
ghrelin
to
rise
unchecked,
leading
to
overeating
later. -
Prioritizing
Sleep:
A
full
night’s
rest
supports
proper
ghrelin
and
leptin
function. -
Managing
Stress:
Reducing
cortisol
levels
helps
prevent
hormonal
disruptions
that
lead
to
cravings.
Managing
Weight

artlist.io/Screenshot,
Make
regular
sleep
your
priority
Make
sleep
a
priority
to
keep
hormones
balanced.
Upon
waking,
eat
a
high-protein
breakfast
and
practice
mindful
eating.
Don’t
crash
diet,
as
doing
so
can
harm
the
health
and
lead
to
high
ghelin
levels.
A
healthy
diet
that
leads
to
slow
weight
loss
over
time
is
best.
Exercise
increases
leptin
sensitivity
while
promoting
ghrelin
regulation
through
stress
reduction.
Dehydrated
people
often
turn
to
food
when
they
need
more
water.
Furthermore,
people
must
maintain
a
meal
schedule
to
manage
their
ghrelin
levels.
When
eating,
they
need
to
focus
on
consuming
whole
foods
that
will
help
with
hormone
regulation.
Many
people
are
unaware
of
the
role
of
hormones
in
weight
management.
They
focus
on
counting
calories
and
exercising
to
bring
their
weight
down.
They
may
not
see
the
desired
results
if
the
hormones
aren’t
balanced.
When
the
hormones
are
balanced,
a
person
can
work
with
their
body
to
develop
healthy
eating
habits
and
maintain
their
desired
weight.
A
balanced
approach
will
consider
the
body’s
signals,
which
is
essential
to
overall
health.
FAQs
Last
Words
Appetite
is
influenced
by
multiple
factors,
including
hormones,
hydration,
environment,
and
lifestyle
choices.
Paying
attention
to
these
signals
helps
people
maintain
a
healthy
relationship
with
food.
Small
adjustments,
such
as
prioritizing
hydration,
choosing
whole
foods,
and
managing
stress,
can
make
appetite
control
more
effective
and
sustainable.